Tel: 01763 262333
Ultra-micropore Analysis
The
term
ultra-micropore,
sometimes
also
super-micropore,
has
become
commonly
used
to
describe
pores
smaller
than
1nm
diameter
(micropores
in
general
are
those
smaller
than
2nm
diameter).
Ultra-micropores
are
commonly
present
in
materials
such
as
activated
carbons,
carbon
nanotubes,
zeolites,
metal
organic
frameworks
(MOFs),
zeolitic
imidazolate
frameworks
(ZIFs)
and
covalent
organic
frameworks
(COFs).
Their
presence
is
often
fundamental
to
applications
and
can
be
extremely
influential
to
capacity,
activity,
adsorption
behaviour,
functionality
and
accessibility.
Typical
applications
include
battery
materials,
adsorbents
and
filters,
catalysts
and
gas
storage
/
sequestration
materials.
Whilst
micropores
are
frequently
required,
their
specific
size
and
volume
must
be
tightly
controlled
in
order
to
maximise
performance
characteristics.
Micropores of the wrong size may cause poor performance or product failure due to low capacity, inaccessibility or pore blocking.
Using
the
most
recent,
state-of-the-art
instrumentation
it
is
possible
to
fully
characterise
micropores
for
their
volume,
surface
area
and
size
distribution.
Together
these
describe
the
porous
nature
of
a
material
and
allow
for
the
relationships
with
material
selection
and
performance
to
be
established.
It
is
then
possible
to
define
the
specific
porous
characteristics
required
from
material
selection,
design,
production
or
regeneration.
Key Applications
Micropore size distribution, volume and pore area for:
Adsorbent capacity, accessibility and retention
Sequestration capacity, accessibility and retention
Gas storage capacity, accessibility and retention
Catalyst efficiency and activity
Battery electrode efficiency, activity and charge / discharge ability
Filter efficiency and efficacy
Determination of regeneration conditions and efficiency
Investigations of atypical performance: effects of low capacity and retention
Investigations of product failure: pore blocking
Identification of optimum characteristics and selection of materials
Determination of production and fabrication conditions
At
MCA
Services
we
use
the
latest,
state-of-the-art
Micromeritics
3Flex
instrument
for
micropore
analysis
which
applies
the
volumetric
method
for
the
measurement
of
adsorption
isotherms.
Nitrogen
is
most
commonly
used
as
the
adsorbate
with
excellent
results
and
the
capability
of
extending
analyses
to
measure
data
in
the
mesopore
region.
Combined
micropore
and
mesopore
analyses
are,
therefore,
possible
in
a
single
analysis
and
extensive
data
reduction
and
reporting
methods
can
be
employed
to
characterise
each.
With
some
sample
materials,
when
unfavourable
interactions
between
nitrogen
and
the
sample
surface
are
area
likely,
it
is
preferable
to
select
an
alternative
adsorbate.
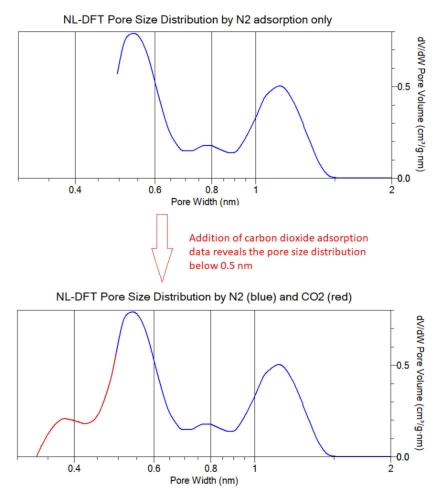
In
such
cases argon adsorption is a suitable analytical method.
However,
when
samples
contain
ultra-micropores
smaller
than
approximately
0.5nm,
nitrogen
and
argon
adsorption
become
problematic
due
to
slow
or
incomplete
accessibility
to
the
smallest
pores
at
the
analysis
temperature.
In
such
cases,
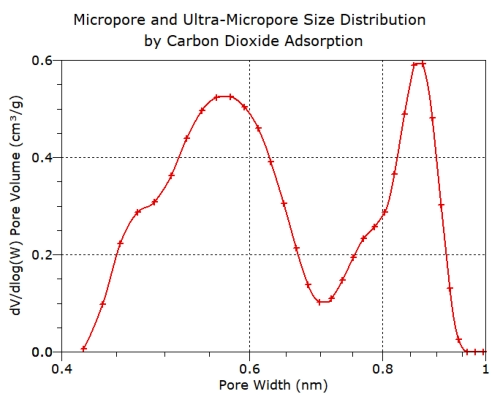
CO
2
adsorption
is
recommended
as
this
can
be
used
to
characterise
pores
as
in
the
range
0.32
-
1.0
nm
diameter
(depending
on
analysis
temperature).
It
is
also
possible
to
combine
CO
2
adsorption isotherms with those of N
2
or Ar to obtain a complete pore characterisation throughout the micropore and mesopore ranges.
Analytical Options and Highlights
Nitrogen adsorption isotherms for micropore and mesopore characterisation
Argon adsorption isotherms for micropore and mesopore characterisation
Carbon dioxide adsorption isotherms for ultra- micropore characterisation
Nitrogen adsorption at 77K
Argon adsorption at 77K or 87K
Carbon dioxide adsorption at 258 – 298 K
Micropore size distribution data (graphical and numerical)
Micropore volume and surface area data (graphical and numerical)
Combination of CO
2
and N
2
or Ar data for complete characterisation
Data reduction by DFT and NL-DFT methods
Comprehensive degassing options
The
Micromeritics
3Flex
is
an
extremely
powerful
instrument
with
cutting
edge
technology
and
a
wealth
of
information
can
be
obtained
from
comprehensive
data
reduction
software.
Combined
with
our
decades
of
experience
the
maximum
information
about
your
samples
can
be
obtained
from
a
single
analysis.
At
MCA
Services
we
are
always
happy
to
advise
the
best
analytical
option
for
your
particular
samples,
applications
and
requirements.
We
also
routinely
assist
in
data
interpretation:
selecting
the
most
pertinent
reporting
data
and
relating
porous
characteristics
to
your specific materials and requirements.
Ultra-micropore Analysis
The
term
ultra-micropore,
sometimes
also
super-micropore,
has
become
commonly
used
to
describe
pores
smaller
than
1nm
diameter
(micropores
in
general
are
those
smaller
than
2nm
diameter).
Ultra-micropores
are
commonly
present
in
materials
such
as
activated
carbons,
carbon
nanotubes,
zeolites,
metal
organic
frameworks
(MOFs),
zeolitic
imidazolate
frameworks
(ZIFs)
and
covalent
organic
frameworks
(COFs).
Their
presence
is
often
fundamental
to
applications
and
can
be
extremely
influential
to
capacity,
activity,
adsorption
behaviour,
functionality
and
accessibility.
Typical
applications
include
battery
materials,
adsorbents
and
filters,
catalysts
and
gas
storage
/
sequestration
materials.
Whilst
micropores
are
frequently
required,
their
specific
size
and
volume
must
be
tightly
controlled
in
order
to
maximise
performance
characteristics.
Micropores
of
the
wrong
size
may
cause
poor
performance
or
product
failure
due
to
low
capacity, inaccessibility or pore blocking.
Using
the
most
recent,
state-of-the-art
instrumentation
it
is
possible
to
fully
characterise
micropores
for
their
volume,
surface
area
and
size
distribution.
Together
these
describe
the
porous
nature
of
a
material
and
allow
for
the
relationships
with
material
selection
and
performance
to
be
established.
It
is
then
possible
to
define
the
specific
porous
characteristics
required
from
material selection, design, production or regeneration.
Key Applications
Micropore size distribution, volume and pore area for:
Adsorbent capacity, accessibility and retention
Sequestration capacity, accessibility and retention
Gas storage capacity, accessibility and retention
Catalyst efficiency and activity
Battery efficiency, activity and charge / discharge ability
Filter efficiency and efficacy
Determination of regeneration conditions and efficiency
Investigations of atypical performance:
effects of low capacity and retention
Investigations of product failure: pore blocking
Identification of optimum characteristics and materials selection
Determination of production and fabrication conditions
At
MCA
Services
we
use
the
latest,
state-of-the-art
Micromeritics
3Flex
instrument
for
micropore
analysis
which
applies
the
volumetric
method
for
the
measurement
of
adsorption
isotherms.
Nitrogen
is
most
commonly
used
as
the
adsorbate
with
excellent
results
and
the
capability
of
extending
analyses
to
measure
data
in
the
mesopore
region.
Combined
micropore
and
mesopore
analyses
are,
therefore,
possible
in
a
single
analysis
and
extensive
data
reduction
and
reporting
methods
can
be
employed
to
characterise
each.
With
some
sample
materials,
when
unfavourable
interactions
between
nitrogen
and
the
sample
surface
are
area
likely,
it
is
preferable
to
select
an
alternative
adsorbate.
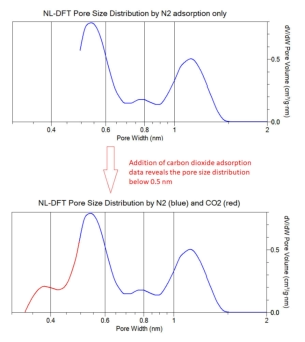
In
such
cases
argon
adsorption
is
a
suitable
analytical
method.
However,
when
samples
contain
ultra-micropores
smaller
than
approximately
0.5nm,
nitrogen
and
argon
adsorption
become
problematic
due
to
slow
or
incomplete
accessibility
to
the
smallest
pores
at
the
analysis
temperature.
In
such
cases,
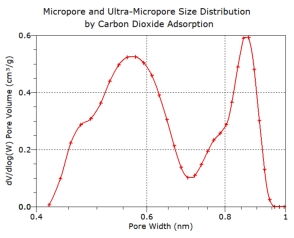
CO2
adsorption
is
recommended
as
this
can
be
used
to
characterise
pores
as
in
the
range
0.32
-
1.0
nm
diameter
(depending
on
analysis
temperature).
It
is
also
possible
to
combine
CO2
adsorption
isotherms
with
those
of
N2
or
Ar
to
obtain
a
complete
pore
characterisation
throughout
the
micropore
and
mesopore
ranges.
Analytical Options and Highlights
Nitrogen adsorption for micropore and mesopore characterisation
Argon adsorption for micropore and mesopore characterisation
Carbon dioxide isotherms for ultra- micropore characterisation
Nitrogen adsorption at 77K
Argon adsorption at 77K or 87K
Carbon dioxide adsorption at 258 – 298 K
Micropore size distribution data (graphical and numerical)
Micropore volume and surface area data
Combination of CO
2
and N
2
or Ar data
Data reduction by DFT and NL-DFT methods
Comprehens
ive degassing options
The
Micromeritics
3Flex
is
an
extremely
powerful
instrument
with
cutting
edge
technology
and
a
wealth
of
information
can
be
obtained
from
comprehensive
data
reduction
software.
Combined
with
our
decades
of
experience
the
maximum
information
about
your
samples
can
be
obtained
from
a
single
analysis.
At
MCA
Services
we
are
always
happy
to
advise
the
best
analytical
option
for
your
particular
samples,
applications
and
requirements.
We
also
routinely
assist
in
data
interpretation:
selecting
the
most
pertinent
reporting
data
and
relating
porous
characteristics
to
your specific materials and requirements.
















