Tel: 01763 262333
Temperature Programmed Analytical Options
Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD)
Temperature Programmed Reduction (TPR)
Temperature Programmed Oxidation (TPO)
Temperature
programmed
analyses
are
part
of
our
suite
of
chemisorption
options,
used
to
investigate
reduction,
oxidation,
desorption
and
decomposition
as
a
function
of
temperature.
Traditionally
these
have
been
applied
to
the
catalysis
sector
where
the
understanding
of
surface
reactions
are
fundamental
to
the
development
and
regeneration
of
high
efficiency
systems.
The
use
of
these
techniques
is
often
extended
to
other
sectors
and
applications,
wherever
the
behaviour
of
oxidisable
or
reducible
species
is
of
importance
or
for
the
study
and
development
of
adsorbents and filter materials.
Temperature
programmed
analyses
at
MCA
Services
are
undertaken
using
our
state-of-the-art
Micromeritics
AutoChem
instrument,
capable
of
analyses
from
sub-ambient
temperature
to
1100
°C.
Furthermore,
this
instrument
provides
tremendous
scope
for
accurate
selection
and
control
over
analytical
parameters
such
as
gas
flow
rate,
temperature
ramp
rate
and
temperature
holding
ranges.
The
instrument
detector
is
always
calibrated to match specific analytical parameters, ensuring the accurate calculation of specific active gas consumption.
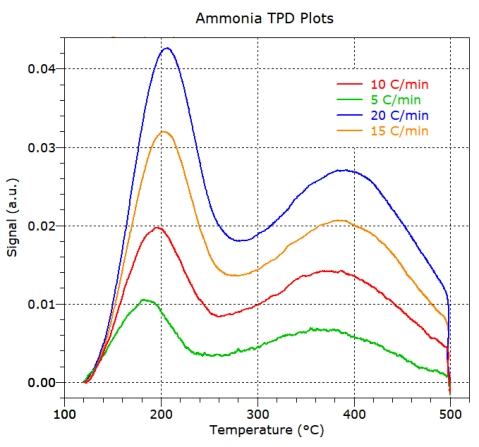
Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD)
Temperature
programmed
desorption
is
used
to
study
the
temperature
dependence
and
strength
of
interaction
between
a
sample
surface
and
a
probe
molecule.
Typical
probe
molecules
include
H2,
CO
and
NH3,
although
others,
including
vapours,
can
also
be
applied
in
order
to
investigate
specific
systems.
Initial
adsorption,
either
physical
or
chemical,
is
usually
conducted
at
ambient
temperature,
although
sub-ambient
conditions
can
also
be
applied.
The
desorption
process
is
then
measured
with
steady
increasing
sample
temperature
under
inert
gas
flow.
Recording
the
temperature
at
which
desorption
occurs
and
accurately
measuring
the
volume
of
gas
desorbing
allows
for
the
determination
of
the
number
and
strength
of
active
adsorption
sites
on
a
sample
surface.
Temperature
programmed
desorption
can
also
be
extended
to
investigate
sample
materials
when
the
adsorption
/
desorption
processes
are
significant
to
performance,
for
example
effectiveness
and
regeneration of adsorbents, filter materials and catalysts.
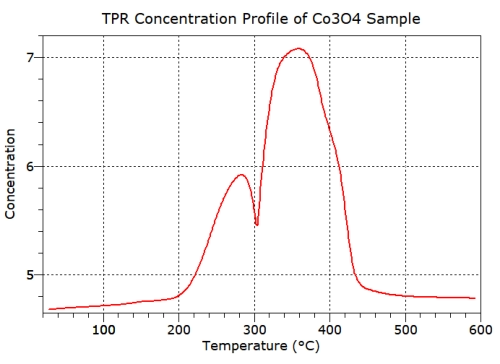
Temperature Programmed Reduction (TPR)
Temperature
programmed
reduction
is
used
to
investigate
the
reducibility
of
a
species
and
can
be
applied
to
metals
and
metal
compounds
such
as
oxides
in
both
supported
and
un-supported
forms.
Historically
very
important
to
the
study
of
catalysts,
TPR
can
be
applied
to
a
wide
variety
of
metallic
and
supported
metallic
species
when
reduction
behaviour
requires
understanding.
The
analytical
process
involves
heating
a
sample
at
a
steady
rate,
to
a
maximum
of
1100
°C,
in
a
stream
of
reducing
gas,
typically
low
concentration
hydrogen
or
carbon
monoxide
balanced
with
an
inert
carrier.
Reduction
of
the
sample
is
then
recorded
using
a
thermal
conductivity
detector
(TCD)
as
the
concentration
of
the
reducing
gas
component
falls
as
it
is
consumed
during
reduction
of
the
sample.
At
MCA
Services,
the
TCD
is
calibrated
with
respect
to
reducing
gas
concentration
which
allows
for
the
calculation
of
active
gas
consumption
during
the
reduction
process.
Results
then
include
quantified
graphical
representations
of
the
reduction
process
in
relation
to
temperature
and
numerical
reducing
gas
consumption
data.
TPR,
therefore,
provides
important
information
regarding
reduction
temperature
and
gas
consumption
which
can
be
extended
to
the
identification
of
the
number
of
reducible
species
and
insight
into
the
reduction
sequence
via
intermediate
species.
This
information
is
important
to
many
process
during
application and regeneration and to the understanding of support materials, which can profoundly affect reduction behaviour.
Temperature Programmed Oxidation (TPO)
Analogous
to
TPR,
temperature
programmed
oxidation
is
applied
to
the
study
of
oxidisable
species
on
a
material
surface.
The
analytical
process
is
very
similar
to
that
of
TPR
with
oxygen
replacing
the
reducing
gas
species
in
the
carrier
stream.
Similar
data
is
also
obtained,
the
TCD
again
being
accurately
calibrated
for
oxygen
consumption,
allowing
for
the
quantified
determination
of
the
number
and
extent
of
oxidisable
species
on
the
sample
surface.
Classic
applications
of
TPO
are
within
the
catalysis
and
electro-catalysis
sectors,
whereby
it
is
very
useful
for
investigating
coking
during
use
for
many
processes
involving
hydrocarbons.
TPO
also
can
be
applied
to
many
systems
when
the
process
of
oxidation
is
of
importance,
including
stages
of
chemical
product and process development in order to maximise efficiency and yield.
At
MCA
Services
we
have
decades
of
experience
in
the
analysis
and
characterisation
of
materials
by
chemisorption
techniques
and
are
always
happy
to
discuss
specific
samples
and
applications.
The
flexibility
of
our
analytical
options
combined
with
our
expertise
ensures
that
the
most
appropriate
analytical
test,
or
combination
of
tests,
are
selected
for
your
particular
sample,
application
and
requirements.
We
also
provide
assistance
with
the
interpretation
of
results
and
more
information
about
these
analytical
options
and
the
background
operation
and
theory
can
be
found on our YouTube channel.
Temperature Programmed Analytical Options
Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD)
Temperature Programmed Reduction (TPR)
Temperature Programmed Oxidation (TPO)
Temperature
programmed
analyses
are
part
of
our
suite
of
chemisorption
options,
used
to
investigate
reduction,
oxidation,
desorption
and
decomposition
as
a
function
of
temperature.
Traditionally
these
have
been
applied
to
the
catalysis
sector
where
the
understanding
of
surface
reactions
are
fundamental
to
the
development
and
regeneration
of
high
efficiency
systems.
The
use
of
these
techniques
is
often
extended
to
other
sectors
and
applications,
wherever
the
behaviour
of
oxidisable
or
reducible
species
is
of
importance
or
for
the
study
and
development of adsorbents and filter materials.
Temperature
programmed
analyses
at
MCA
Services
are
undertaken
using
our
state-of-the-art
Micromeritics
AutoChem
instrument,
capable
of
analyses
from
sub-ambient
temperature
to
1100
°C.
Furthermore,
this
instrument
provides
tremendous
scope
for
accurate
selection
and
control
over
analytical
parameters
such
as
gas
flow
rate,
temperature
ramp
rate
and
temperature
holding
ranges.
The
instrument
detector
is
always
calibrated
to
match
specific
analytical
parameters,
ensuring
the
accurate calculation of specific active gas consumption.
Temperature Programmed Desorption (TPD)
Temperature
programmed
desorption
is
used
to
study
the
temperature
dependence
and
strength
of
interaction
between
a
sample
surface
and
a
probe
molecule.
Typical
probe
molecules
include
H2,
CO
and
NH3,
although
others,
including
vapours,
can
also
be
applied
in
order
to
investigate
specific
systems.
Initial
adsorption,
either
physical
or
chemical,
is
usually
conducted
at
ambient
temperature,
although
sub-ambient
conditions
can
also
be
applied.
The
desorption
process
is
then
measured
with
steady
increasing
sample
temperature
under
inert
gas
flow.
Recording
the
temperature
at
which
desorption
occurs
and
accurately
measuring
the
volume
of
gas
desorbing
allows
for
the
determination
of
the
number
and
strength
of
active
adsorption
sites
on
a
sample
surface.
Temperature
programmed
desorption
can
also
be
extended
to
investigate
sample
materials
when
the
adsorption
/
desorption
processes
are
significant
to
performance,
for
example
effectiveness
and
regeneration
of
adsorbents,
filter
materials and catalysts.
Temperature Programmed Reduction (TPR)
Temperature
programmed
reduction
is
used
to
investigate
the
reducibility
of
a
species
and
can
be
applied
to
metals
and
metal
compounds
such
as
oxides
in
both
supported
and
un-supported
forms.
Historically
very
important
to
the
study
of
catalysts,
TPR
can
be
applied
to
a
wide
variety
of
metallic
and
supported
metallic
species
when
reduction
behaviour
requires
understanding.
The
analytical
process
involves
heating
a
sample
at
a
steady
rate,
to
a
maximum
of
1100
°C,
in
a
stream
of
reducing
gas,
typically
low
concentration
hydrogen
or
carbon
monoxide
balanced
with
an
inert
carrier.
Reduction
of
the
sample
is
then
recorded
using
a
thermal
conductivity
detector
(TCD)
as
the
concentration
of
the
reducing
gas
component
falls
as
it
is
consumed
during
reduction
of
the
sample.
At
MCA
Services,
the
TCD
is
calibrated
with
respect
to
reducing
gas
concentration
which
allows
for
the
calculation
of
active
gas
consumption
during
the
reduction
process.
Results
then
include
quantified
graphical
representations
of
the
reduction
process
in
relation
to
temperature
and
numerical
reducing
gas
consumption
data.
TPR,
therefore,
provides
important
information
regarding
reduction
temperature
and
gas
consumption
which
can
be
extended
to
the
identification
of
the
number
of
reducible
species
and
insight
into
the
reduction
sequence
via
intermediate
species.
This
information
is
important
to
many
process
during
application
and
regeneration
and
to
the
understanding
of
support
materials,
which
can
profoundly affect reduction behaviour.
Temperature Programmed Oxidation (TPO)
Analogous
to
TPR,
temperature
programmed
oxidation
is
applied
to
the
study
of
oxidisable
species
on
a
material
surface.
The
analytical
process
is
very
similar
to
that
of
TPR
with
oxygen
replacing
the
reducing
gas
species
in
the
carrier
stream.
Similar
data
is
also
obtained,
the
TCD
again
being
accurately
calibrated
for
oxygen
consumption,
allowing
for
the
quantified
determination
of
the
number
and
extent
of
oxidisable
species
on
the
sample
surface.
Classic
applications
of
TPO
are
within
the
catalysis
and
electro-catalysis
sectors,
whereby
it
is
very
useful
for
investigating
coking
during
use
for
many
processes
involving
hydrocarbons.
TPO
also
can
be
applied
to
many
systems
when
the
process
of
oxidation
is
of
importance,
including
stages
of
chemical
product
and
process
development
in
order
to
maximise
efficiency and yield.
At
MCA
Services
we
have
decades
of
experience
in
the
analysis
and
characterisation
of
materials
by
chemisorption
techniques
and
are
always
happy
to
discuss
specific
samples
and
applications.
The
flexibility
of
our
analytical
options
combined
with
our
expertise
ensures
that
the
most
appropriate
analytical
test,
or
combination
of
tests,
are
selected
for
your
particular
sample,
application
and
requirements.
We
also
provide
assistance
with
the
interpretation
of
results
and
more
information
about
these
analytical
options
and
the
background
operation
and
theory
can be found on our YouTube channel.
















