Expertise in the Physical
Characterisation of Materials

MCA Services
Unit 1A Long Barn, North End, Meldreth, Cambridgeshire SG8 6NT UK
01763 262333
© MCA Services




Chemisorption Analysis (Chemical Adsorption)
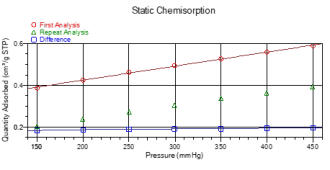
Static Chemisorption
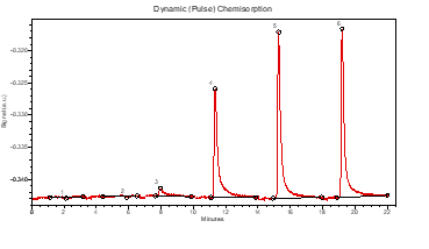
Dynamic (Pulse) Chemisorption
CO, H2 and O2 Chemisorption Options
Chemical
adsorption,
or
chemisorption
analysis,
concerns
the
formation
of
chemical
bonds
between
an
adsorptive
gas
and
the
active
surface
sites
on
a
sample.
Chemisorption
is
particularly
suited
to
the
characterisation
and
optimisation
of
catalysts.
Chemisorption
is
used
to
determine
the
surface
area,
dispersion
and
crystallite
size
of
active
metals
in
a
catalyst.
These
essentially
provide
critical
information
regarding
the
surface
chemistry
of
a
sample
and
the
availability
of
the
catalytically-active
constituents.
With
this
information
it
is
possible
to
assess
the
efficiency
of
a
catalyst
sample
for
a
given
chemical
reaction,
which
is
critical
to
the
development
of
catalytic
materials.
Alternatively,
chemisorption can be applied to functioning catalysts in order to monitor degradation over time and assess the success of re-generation.
Key Information.
•
Static chemisorption analysis
•
Dynamic (pulse) analysis
•
Choice of analysis temperature
•
Choice of in-situ pre-reduction conditions
•
Carbon monoxide chemisorption
•
Hydrogen chemisorption
•
Oxygen chemisorption
•
Other probe gases available in request
•
Metal dispersion (%)
•
Metallic (active) surface area of metal
•
Metallic (active) surface area of sample
•
Crystallite size (nm)
•
At
MCA
Services
we
offer
two
different
chemisorption
techniques,
both
using
the
state-of-the-art
Micromeritics
3Flex
TCD
Chemisorption
instrument.
Static
chemisorption
is
undertaken
at
a
constant
temperature
over
a
range
of
relative
pressures
with
two
adsorption
isotherms
being
measured.
The
first
isotherm
is
due
to
both
chemically
(strong)
and
physically
(weak)
adsorbed
species
whereas
the
second
isotherm
is
due
solely
to
physisorbed
species.
The
volume
chemically
adsorbed
onto
the
sample
can
then
be
determined
and
applied
to
calculation
of
active
metal area, dispersion, etc.
Dynamic,
or
pulse
chemisorption,
is
undertaken
at
atmospheric
pressure
using
a
flowing
gas
technique.
Successive
injections
of
a
calibrated
volume
of
adsorptive
gas
are
made
to
the
sample
and
a
TCD
(Thermal
Conductivity
Detector)
is
used
to
measure
the
volume
of
adsorptive
gas
which
is
not
chemisorbed
onto
the
sample.
The
sample
is
saturated
with
adsorptive
gas
when
a
complete
injection
is
passed
through
to
the
TCD, the volume of adsorptive chemisorbed can then be calculated and applied the to calculation of active metal area, dispersion, etc.
Alternative
chemisorption
analyses
include
a
range
of
temperature
programmed
techniques,
such
as
TPD,
TPR
and
TPD,
please
see
our
Temperature Programmed Analyses page for more details.





Expertise in the Physical
Characterisation of Materials
MCA Services
Unit 1A Long Barn, North End,
Meldreth, Cambridgeshire SG8 6NT UK
01763 262333
© MCA Services




Chemisorption Analysis (Chemical Adsorption)
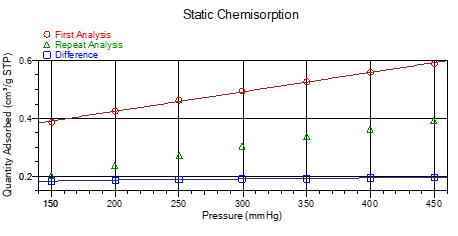
Static Chemisorption
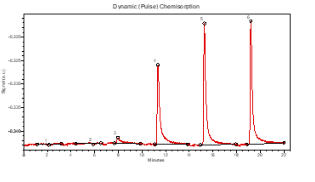
Dynamic (Pulse) Chemisorption
CO, H2 and O2 Chemisorption Options
Chemical
adsorption,
or
chemisorption
analysis,
concerns
the
formation
of
chemical
bonds
between
an
adsorptive
gas
and
the
active
surface
sites
on
a
sample.
Chemisorption
is
particularly
suited
to
the
characterisation
and
optimisation
of
catalysts.
Chemisorption
is
used
to
determine
the
surface
area,
dispersion
and
crystallite
size
of
active
metals
in
a
catalyst.
These
essentially
provide
critical
information
regarding
the
surface
chemistry
of
a
sample
and
the
availability
of
the
catalytically-active
constituents.
With
this
information
it
is
possible
to
assess
the
efficiency
of
a
catalyst
sample
for
a
given
chemical
reaction,
which
is
critical
to
the
development
of
catalytic
materials.
Alternatively,
chemisorption
can
be
applied
to
functioning
catalysts
in
order
to
monitor degradation over time and assess the success of re-generation.
Key Information.
•
Static chemisorption analysis
•
Dynamic (pulse) analysis
•
Choice of analysis temperature
•
Choice of in-situ pre-reduction conditions
•
Carbon monoxide chemisorption
•
Hydrogen chemisorption
•
Oxygen chemisorption
•
Other probe gases available in request
•
Metal dispersion (%)
•
Metallic (active) surface area of metal
•
Metallic (active) surface area of sample
•
Crystallite size (nm)
•
At
MCA
Services
we
offer
two
different
chemisorption
techniques,
both
using
the
state-of-the-art
Micromeritics
3Flex
TCD
Chemisorption
instrument.
Static
chemisorption
is
undertaken
at
a
constant
temperature
over
a
range
of
relative
pressures
with
two
adsorption
isotherms
being
measured.
The
first
isotherm
is
due
to
both
chemically
(strong)
and
physically
(weak)
adsorbed
species
whereas
the
second
isotherm
is
due
solely
to
physisorbed
species.
The
volume
chemically
adsorbed
onto
the
sample
can
then
be
determined
and
applied
to
calculation
of
active
metal area, dispersion, etc.
Dynamic,
or
pulse
chemisorption,
is
undertaken
at
atmospheric
pressure
using
a
flowing
gas
technique.
Successive
injections
of
a
calibrated
volume
of
adsorptive
gas
are
made
to
the
sample
and
a
TCD
(Thermal
Conductivity
Detector)
is
used
to
measure
the
volume
of
adsorptive
gas
which
is
not
chemisorbed
onto
the
sample.
The
sample
is
saturated
with
adsorptive
gas
when
a
complete
injection
is
passed
through
to
the
TCD,
the
volume
of
adsorptive
chemisorbed
can
then
be
calculated
and
applied the to calculation of active metal area, dispersion, etc.
Alternative
chemisorption
analyses
include
a
range
of
temperature
programmed
techniques,
such
as
TPD,
TPR
and
TPD,
please
see
our
Temperature Programmed Analyses page for more details.


01763262333